Sequence Analysis¶
Evol component of ProDy package brought new fast, flexible, and efficient features for handling multiple sequence alignments and analyzing sequence evolution. Here, we just give a brief introduction to these features. For more detailed examples, see Evol Tutorial.
In [1]: from prody import *
In [2]: from pylab import *
In [3]: ion()
Access Pfam¶
First, let’s fetch an MSA file from Pfam database:
In [4]: filename = fetchPfamMSA('pkinase', alignment='seed')
In [5]: filename
We downloaded the seed alignment for Protein Kinase (Pkinase) family.
Parse MSA¶
As you might guess, we will parse this file using parseMSA() function:
In [6]: msa = parseMSA('pkinase_seed.sth')
In [7]: msa
Out[7]: <MSA: pkinase_seed (38 sequences, 419 residues)>
Sequences¶
You can access Sequence objects by indexing MSA:
In [8]: seq = msa[0]
In [9]: seq
Out[9]: <Sequence: TTK_HUMAN (pkinase_seed[0]; length 419; 267 residues and 152 gaps)>
In [10]: print(seq)
YSILKQIGSGGSSKV..FQVLN.EKKQIYAIKYVNLEEADNQTL......DSYRNEIAYLNKLQQ.HSDKIIRLYDYEIT.............DQYIY..MVMECGNID.....LNSWLK.......KKKS.IDPW.......ERK.SYWKNMLEAVHTIH.QHG...IVHSDLKPANFLIV............DGM........LKLIDFGIANQMQPDTTS................VVKDSQVGTVNYMPPEAIKDMSSSRENGKS...KSKISPKSDVWSLGCILYYMTYGKTPFQQIINQISKLHAIID.................................PNHEI.........................EFPDIPEKDLQDVLKCCLKRDPKQRIS.....IPELLAHPYV
You can also slice MSA objects and iterate over sequences:
In [11]: for seq in msa[:4]:
....: print(repr(seq))
....:
<Sequence: TTK_HUMAN (pkinase_seed[0]; length 419; 267 residues and 152 gaps)>
<Sequence: MKK1_YEAST (pkinase_seed[1]; length 419; 268 residues and 151 gaps)>
<Sequence: STE7_YEAST (pkinase_seed[2]; length 419; 276 residues and 143 gaps)>
<Sequence: BYR1_SCHPO (pkinase_seed[3]; length 419; 255 residues and 164 gaps)>
Analysis¶
Evol component includes several functions for calculating conservation and
coevolution properties of amino acids, which are shown in Evol Tutorial.
Here, let’s take a look at calcMSAOccupancy() and
showMSAOccupancy() functions:
In [12]: occ = calcMSAOccupancy(msa, count=True)
In [13]: occ.min()
Out[13]: 1.0
This shows that an amino acid is present only in one of the sequences in the MSA.
In [14]: showMSAOccupancy(msa, count=True);
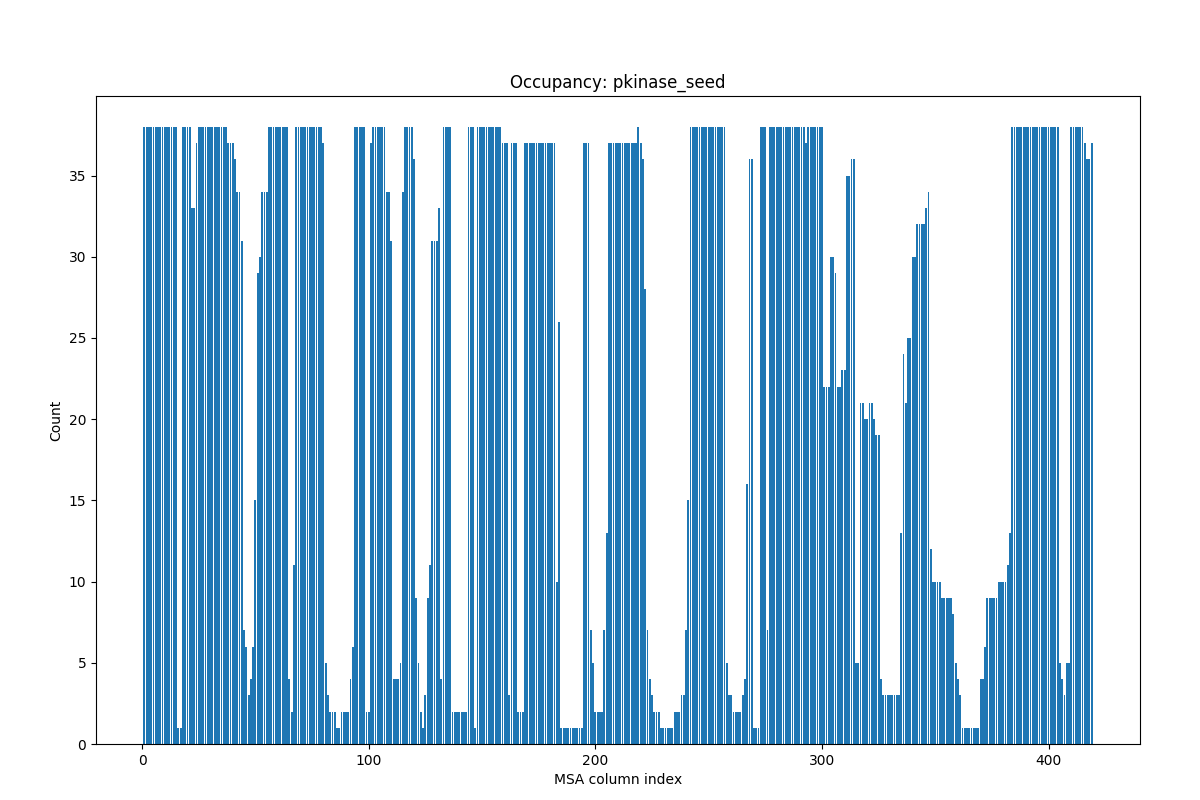
You see that many residues are not present in all sequences. You will see how to refine such MSA instances in Evol Tutorial.
